If you’re into ketogenic nutrition, protein can be a tremendous ally. In fact, the best protein powders for keto diets complement its low-carb, medium-protein, and high-fat focus.
Meeting one’s daily protein requirements can be a daunting challenge, even for Keto dieters. Not to worry, protein supplements help in this regard. They are the most convenient source of this macronutrient – with them around, you can consume protein anytime and anywhere.
Table of Contents
Keto Diet Basics

The Keto Diet has several impressive benefits.
The Keto Diet – also known as the ketogenic diet, low-carb diet, and a low-carb, high-fat diet – de-emphasizes carbohydrates so the body produces ketones (an organic compound and by-product of the body which breaks down fat into energy) in the liver.
A high-carbohydrate nutrition plan enables the body to produce glucose (a simple sugar which the body uses as an energy source) and insulin (an anabolic hormone which helps the body maximize glucose absorption).
Here, the body doesn’t utilize fats, so it stores them instead. On the other hand, when an individual lowers his or her carb intake, the body goes into a state known as ketosis – a process which the body undergoes when food intake is insufficient. Consider it a form of survival mode, contingency plan, or Plan B.
The end goal of the Keto Diet “is to force the body into this metabolic state. We don’t do this through starvation of calories, but starvation of carbohydrates,” per its official website.
The same source says the body adjusts incredibly to whatever food source it consumes. When one puts a premium on fat consumption and decreases carbohydrate intake considerably, the body will burn ketones for energy.
Keto Diet Benefits
The Keto Diet’s official website says, “Optimal ketone levels offer many health, weight loss, physical, and mental performance benefits.”
From a cellular point of view, a restricted carbohydrate intake allows the body to react “as if it is fasting,” per the same source. This, in turn, creates new energy pathways. One of these is ketogenesis, whose by-product is an alternative energy source known as a ketone body.
The body’s cells use these ketone bodies as fuel (except the liver and red blood cells). Not only do these ketones provide an efficient energy source, but they also help boost mitochondrial function. The end result: increased protection for the brain’s neuron cells.
Carbohydrate restriction also helps activate a cell process known as autophagy. Long story short, it helps boost cellular function and keep inflammation at bay. That’s just the proverbial tip of the iceberg. The Keto Diet has several other important health benefits which should appeal to a large demographic.
Acne Control
Some individuals have acne issues. This can be inconvenient and embarrassing, to say the least. Making the switch to the Keto Diet helps boost skin health and ward off acne.
In fact, the journal Skin Pharmacology and Physiology’s January 3, 2012 issue (via ResearchGate.net) says, “Ketosis, which is a perfectly physiological process in man, reduces several markers of inflammation, and by reducing insulinemia, which also affects the IGF-1 pathway, it could be effective in reducing the severity and progression of acne.”
Insulin Resistance
If a person has insulin resistance issues, it may affect his or her blood sugar levels sooner than later. Modern research has vouched for the Keto Diet’s ability to restore insulin levels to a safe range.
As hard evidence, researchers monitored 21 overweight males who completed a study involving a low-carbohydrate, ketogenic diet (LCKD) in December 2005. The journal Nutrition & Metabolism’s (via NCBI.NLM.NIH.gov) issue that month says, “The LCKD improved glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes such that diabetes medications were discontinued or reduced in most participants.” Indeed, the Keto Diet shows great promise in regulating blood sugar levels.
Cholesterol and Blood Pressure Issues
Researchers’ findings reveal the Keto Diet helps regulate triglyceride and cholesterol levels which may result in long-term cardiovascular issues. This nutrition plan also helps ramp up HDL (good cholesterol) levels and keep LDL levels (bad cholesterol) at bay. Cardiologists say that’s a recipe for a healthy heart.
The Keto Diet also has some promise regarding its effect on blood pressure levels. According to the May 9, 2017 issue of Nutrients (via NCBI.NLM.NIH.gov), “A study described an improvement in both systolic and diastolic blood pressure in obese participants when fed a KD (ketogenic diet) during 48 weeks compared to a low-fat diet plus orlistat.”
In addition, physicians associate some blood pressure cases with excess weight. One of the Keto Diet’s goals is weight loss, which may improve blood pressure levels.
Increased Energy Levels
Many people associate a high-carbohydrate diet with increased energy levels. However, a low-carbohydrate ketogenic diet can also produce the same effect. “Fats are shown to be the most effective molecule to burn as fuel,” per the Keto Diet’s official website.
In fact, the journal Nutrients’ July 6, 2014 issue (via NCBI.NLM.NIH.gov) concluded the Keto Diet produces favorable results among endurance athletes. More specifically, it says, “Long-term, high-fat diets may be favorable for aerobic endurance athletes, during the preparatory season, when a high volume and low to moderate intensity of training loads predominate in the training process.”
However, the same source also cautions the public that “low-carbohydrate ketogenic diets decrease the ability to perform high-intensity work, due to decreased glycogen muscle stores and the lower activity of glycolytic enzymes, which is evidenced by a lower LA (lactic acid) concentration and a maximal workload during the last 15 minutes of the high-intensity stage of the exercise protocol.”
The takeaway: the Keto Diet may be a double-edged sword in terms of its effects on high-intensity exercise. If you have any doubts, it’s always best to consult your doctor and nutritionist before going on the Keto Diet or any unfamiliar nutrition plan.
Mental Focus
Some individuals resort to the Keto Diet because they want to increase their mental performance. Ketones are a reliable source of brain fuel. A decreased consumption of carbohydrates wards off huge spikes in blood sugar levels. Plus, higher fatty acid intake help enhance cognitive function. Researchers say these help increase focus.
According to the American Council on Exercise’s official website, “The exact mechanism for which ketogenic diets could be effective is still not clearly understood, but they do show a neuroprotective effect.”
Blood Sugar Regulation
The Keto Diet’s de-emphasis on carbohydrates “helps to restore insulin sensitivity, blood sugar control, and hemoglobin A1c,” per the American Council on Exercise’s official website.
Harvard Medical School’s Dr. Marcelo Campos says, “A ketogenic diet has also been shown to improve blood sugar control for patients with type 2 diabetes.” Clearly, the Keto Diet shows tremendous promise in warding off blood sugar issues. This is also why the best protein powders for keto diets are universally lower in sugar.
Weight Loss
One of the Keto Diet’s main goals is weight loss. There are several principles behind this. For one, the Keto Diet uses fats as a main source of energy. Second, an individual’s insulin levels (the hormone which stores fat) plummet while he or she is on a ketogenic nutrition plan.
“Correctly understood, the ketogenic diet can be a useful tool to treat obesity in the hands of the physician,” per the International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health’s February 11, 2014 issue (via NCBI.NLM.NIH.gov).
Keto Diet Side Effects
While the Keto Diet has several attractive side benefits, it may also produce certain side effects. Individuals who are accustomed to consuming plenty of carbohydrates previously could be affected.
When a person makes a switch to the Keto Diet, he or she is putting his or her body under stress because it is seeking an alternative source of fuel. At first, the body will seek out sugar for this purpose. It is not accustomed to such low carbohydrate and sugar levels. Because of that, a person’s cortisol (stress hormone) levels will increase.
A low-carbohydrate or Keto Diet may also increase one’s ammonia levels. Ammonia is a compound which “may provoke fatigue, especially when untrained subjects exercise for a prolonged period without glucose supplementation,” per The Journal of Physiology’s February 15, 2005 issue (via NCBI.NLM.NIH.gov).
Here are the other potential side effects of the Keto Diet:
- Lower insulin and carbon dioxide levels
- Increased frequency of urination
- Loss of muscle mass and decreased physical performance
- Impaired thyroid function
- Gastrointestinal issues (constipation or diarrhea)
- Bad breath
- Headache, fatigue, and weakness
- Cramps
- Heart palpitations
If these concern you, best to consult your physician before making the switch to the Keto Diet or any unfamiliar nutrition plan — and before taking any of the best protein powders for keto diets.
Nutrition Principles of the Keto Diet
Proponents of the Keto Diet say the food you eat depends on how fast you want to make the transition into a ketogenic state. The lower one’s carbohydrate consumption is, the faster he or she will make this transition.
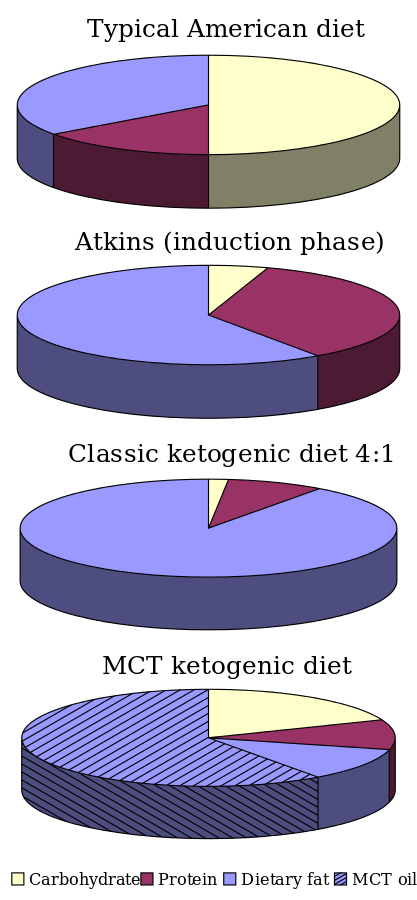
In principle, the Keto Diet is high in fats (roughly 75 percent), moderate in protein (roughly 25 percent), and low in carbohydrates (roughly five percent). It allows somewhere between 20 to 30 net carbs (total dietary carbs less total fiber) daily. However, it encourages lower carb consumption and glucose levels for better overall results.
The Keto Diet limits carbohydrate sources to dairy, nuts, and vegetables. It considers dark, green, and leafy vegetables as the best. Here are some of the best choices for the Keto Diet (each serving is half a cup):
| Vegetable | Net Carbs (total dietary carbs less total fiber) |
| Raw spinach | 0.1 |
| Raw bok choi | 0.2 |
| Romaine lettuce | 0.2 |
| Steamed cauliflower | 0.9 |
| Raw green cabbage | 1.1 |
| Raw cauliflower | 1.4 |
| Broccoli (florets) | 2 |
| Collard greens | 2 |
| Steamed kale | 2.1 |
| Steamed green beans | 2.9 |
Each meal should consist of vegetables, a protein source, and some fats on the side. An example is chicken slathered in olive oil with broccoli and cheese.
Among the carb sources which are off limits on the Keto Diet are bread, pasta, cereals, legumes, beans, potatoes, and fruit (except berries, avocado, star fruit, which one can consume in moderation).
The Keto Diet allows snacking to curb hunger pangs. Smart snack choices include peanut butter, cheese, seeds, and nuts.
The Role of Protein in the Keto Diet

Protein is the macronutrient which helps increase muscle mass, repair muscle tissue, increase satiety, regulate blood sugar levels, improve mood, enhance cognitive function, strengthen bones, improve cardiovascular function, and increase longevity.
The Keto Diet considers protein as an essential component. It encourages moderate protein consumption (around 25 percent of daily nutritional intake). It is not a high-protein diet. To sum things up once gain, the Keto Diet is a high-fat, moderate-protein, and low-carb nutrition plan.
The proponents of the Keto Diet encourage those new to it to regulate their protein intake. Too much protein can keep an individual out of ketosis. Excess protein consumption results in gluconeogenesis, where the body converts amino acids into glucose for energy. This also results in an insulin spike and a decrease in ketone levels in the blood.
Experts say consuming 0.7 to 0.9 grams of protein per pound of lean bodyweight (equal to 1.5 to 2.0 grams of protein per kilogram of lean bodyweight) daily is the ideal range when on a Keto Diet.
Say, for example, a medium-build male weighs 150 lbs. (68 kg.). That means he should consume 105 to 135 grams of protein daily. If he eats three times in a day, that comes down to 35 to 45 grams of protein per meal. If he consumes five meals daily (including snacks), he must consume 21 to 27 grams of protein per meal.
Here are some of the best protein sources for the Keto Diet:
- Beef (ground or roast beef, veal, and steak)
- Fish (catfish, sardines, cod, tuna, salmon, mackerel, trout, halibut)
- Poultry (chicken, turkey, duck, and quail)
- Pork (tenderloin, pork chops, pork loin)
- Goat/lamb
- Eggs
- Shellfish (lobster, oyster, mussel, crab, clam)
Make sure your protein sources come from natural sources. Steer clear of processed meats, which may include unnecessary carbs and sugar.
Best Protein Powders for the Keto Diet
If you’re on the Keto Diet and want an alternative source of protein, protein supplements should help. The best ones are consistent with the Keto Diet’s principles: low-carb, medium-protein, and high-fat. When taking bodybuilding supplements, always bear in mind the 0.7 to 0.9 grams of protein per pound of lean bodyweight (1.5 to 2.0 grams of protein per kilogram of lean body weight) reference range.
Whey Protein
Whey protein is one of the most popular – if not most popular – muscle-building supplement among bodybuilding enthusiasts. It takes up 20 percent of cow’s milk (the other 80 percent is casein).

Whey has fast absorption properties – the body typically absorbs it within a maximum of 40 minutes after consumption. It’s an ideal choice for those who want to replenish as soon as possible after a hard workout. Aside from protein powders, you can find whey protein in several post-workout supplements.
There are several types of whey protein. Whey protein isolate (WPI) is 90 to 95 percent protein and has a lower carb content than its whey protein concentrate (WPC) counterpart (which is roughly 70 to 85 percent protein).
One can make a case for WPI as the better Keto Diet protein supplement because of its low carb content. However, WPC has a higher fat content than WPI (bear in mind the Keto Diet places a heavy emphasis on fats), so that tilts the balance.
The takeaway: choose the type of whey which fits your lifestyle better. On a side note, if you have lactose issues, try steering clear of WPC. WPI would be the better choice in that case.
Beef Protein

Beef is one of the ideal protein sources in the Keto Diet. It’s a great natural source of lean protein. Plus, it’s a natural source of creatine, taurine, vitamin B12, vitamin B6, vitamin B3, phosphorus, iron, and selenium.
Beef is also a tremendous source of glutathione, a powerful antioxidant which helps ward off free radicals. While natural beef is a source of fats (particularly saturated fats), its supplement form usually keeps fat levels in check.
Nonetheless, beef protein is a great alternative for individuals who have issues with dairy and eggs. Try supplementing with grass-fed beef protein because it has impressive levels of collagen (the protein found in connective tissue) and gelatin.
Collagen Protein
 Collagen is the protein found in connective tissue. It makes up roughly a third of the human body. You can find collagen in the tendons, gut, muscles, bones, and skin.
Collagen is the protein found in connective tissue. It makes up roughly a third of the human body. You can find collagen in the tendons, gut, muscles, bones, and skin.
Collagen isn’t as popular as, say, whey. However, it is a decent protein source (one serving can yield as much as 25 grams of protein). Hydrolyzed collagen is a also a great source of creatine, which helps increase muscle mass and athletic performance.
Collagen also offers additional health benefits:
- Helps promote weight loss
- Strengthens bones and joints
- Improves sleep quality
- Boosts digestion
- Improves skin, nail, and hair health
- Increases satiety
If neither whey nor beef protein is up your alley, try supplementing with collagen protein while on the Keto Diet. It should help you achieve your fitness goals.
Other Supplements for Keto Dieters
Protein supplements aren’t the only ones which should complement the Keto Diet. Experts recommend several others which should help compensate this nutrition plan’s low-carb, medium-protein, and high-fat approach. Check out which ones are up your alley.
Greens Supplements
The Keto Diet allows consumption of green, leafy vegetables. However, even individuals who follow a ketogenic approach may find incorporating vegetables into their daily nutrition plan challenging. Enter greens supplements – the most convenient way of getting your vegetable fix.
Among the best vegetables for the Keto Diet are spinach, bok choi, lettuce, and cauliflower. When one has no time to cook, taking a greens supplement will go a long way. This product comes in either powder or capsule form, so you can take it anytime and anywhere. You can even add a scoop or two to your protein shake for a healthier concoction.
Bear in mind greens supplements are not supposed to replace whole foods in one’s nutrition plan. That’s exactly what they are – supplements.
Caffeine
Making the switch to the Keto Diet – or any nutritional plan, for that matter – isn’t easy. When you reduce your carbohydrate intake considerably, expect your body to go through a myriad of changes (fatigue and weakness could be among them). Caffeine – arguably the world’s most famous stimulant – should help immensely.
Caffeine won’t only perk you up, but it’ll also help increase your energy levels and boost fat loss. You’ll also enjoy its other proven benefits:
- Improves physical performance
- Regulates blood sugar levels
- Boosts liver function
- Enhances mood and cognitive function
- Keeps free radicals at bay
- Increases longevity
You can see for yourself caffeine isn’t just about energy and fat loss. Clearly, it can be a tremendous ally in your Keto Diet journey.
However, caffeine is a double-edged sword: it may also produce a spike-crash effect, jitters, nervousness, and sleeplessness in some individuals. Overconsumption may also slightly increase one’s cholesterol levels. With these in mind, please take the necessary precautions. Better yet, consult your physician as to how much caffeine you can consume daily.
You can find caffeine in many BCAA and pre-workout supplements. These will give you an edge in your workouts, for sure.
Fiber
Let’s be honest: some individuals just do not like the taste of vegetables. That’s a shame, considering vegetables are a rich source of dietary fiber. If you’re not really big on vegetables, try taking a fiber supplement. Their main advantages: they help regulate digestion and increase satiety. If your main goal on the Keto Diet is to lose weight, a fiber supplement should be a great complement.
A word of caution: many fiber supplements are high in carbohydrates. Make sure to read supplement facts and nutrition labels accordingly before buying any supplement. Try going for one which is high in fats (preferably from good sources such as flaxseeds).
MCT Oil
“MCT” stand for “medium-chain triglycerides.” They’re also known as “MCFAs” or “medium-chain fatty acids.” Long story short, MCTs are essential healthy fats which have a potent fat-burning effect.
Plus, the Charlie Foundation for Ketogenic Therapies’ official website says, “Medium-chain triglycerides produce ketones more easily than long-chain triglycerides (LCT) fat, with certain MCTs bypassing the liver and converting directly into ketones.” Moreover, one teaspoon of MCT oil yields an impressive 14 grams of fats. It sure seems these fit the description of a Keto Diet supplement perfectly.
The body absorbs MCTs faster than long-chain triglycerides because the former are smaller in structure. Because of that, they serve as a rapid fuel source for the brain and muscles. Here are some of the impressive benefits of MCT Oil:
- Wards off free radicals
- Increases energy levels and satiety
- Improves gastrointestinal function
- Helps maintain a healthy weight
- Boosts cognitive function
- Keeps bacterial activity at bay
Perhaps the most popular source of MCT oil is coconut oil, whose fat content is 60 percent medium-chain triglycerides. Other sources of MCT oil include butter, cheese, palm oil, grass-fed whole milk, and grass-fed full-fat yogurt.
Electrolytes
Electrolytes are electrically-charged elements or minerals which help promote optimum nerve and muscle function. They also help maintain the body’s ideal fluid balance and boost hydration. Among the more common ones are phosphate, magnesium, sodium, potassium, and calcium.
It is imperative the body maintains a balanced level of electrolytes for proper water and blood acidity levels. Otherwise, an individual may experience muscle cramps, diarrhea, fatigue, sweating, nausea, and vomiting.
When a person lowers his or her carbohydrate intake drastically, so do his or her electrolyte levels (particularly sodium and potassium). Training hard at the gym while on a Keto Diet makes electrolyte consumption all the more vital. One can find electrolytes in coconut water, sports drinks (just make sure they don’t contain any artificial food colorings), and post-workout supplements.
Protein Supplements and the Keto Diet

The Keto Diet places a heavy emphasis on fats, medium emphasis on protein, and light emphasis on carbs. With that, if you’re on a ketogenic diet plan, protein is still an integral part of your nutrition equation. It bears repeating: try sticking to the 0.7 to 0.9 grams of protein per pound of lean bodyweight (1.5 to 2.0 grams of protein per kilogram of lean bodyweight) reference range for best long-term results.
Depending on your meal frequency on the Keto Diet, expect to consume anywhere between 21 to 45 grams of protein per meal. If you prefer to snack between meals, a good protein supplement not only helps you meet your daily protein requirements, but increase muscle mass and satiety as well. These products will also help you make that important transition from a catabolic (muscle breakdown) to an anabolic (muscle-building) state at the gym.
The key takeaway: whey protein, beef protein, and collagen protein are your best bets while on the Keto Diet. These should help complement your ketogenic nutrition plan perfectly.
Best 5 Protein Powders for Keto Dieters – Reliable, High-Quality Brands
We at Best 5 Supplements have reviewed many protein supplements. We recommend the following protein powders to those who want to get the most out of their Keto Diet plan:
Leave a Reply